380kV Gantries & Gantry Equipment is our first post that is a part of Substation Layout Drawing & Explanation each equipment in a 380kV BSP. Gantries are the tall steel structures at the extreme ends of the yard that serve as termination points for overhead transmission lines (OHTLs) entering the substation at 380kV. In this Guide we will provide you practical substation Gantry area photos that clearly shows each equipment position in substation.
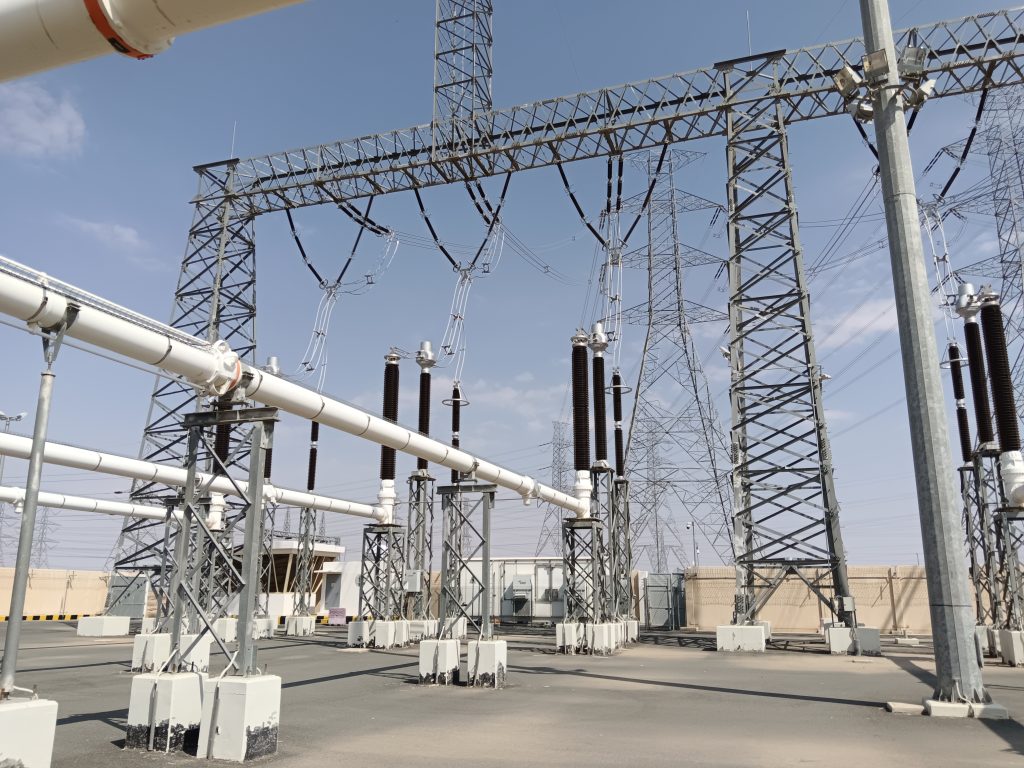
1. 380kV Gantries
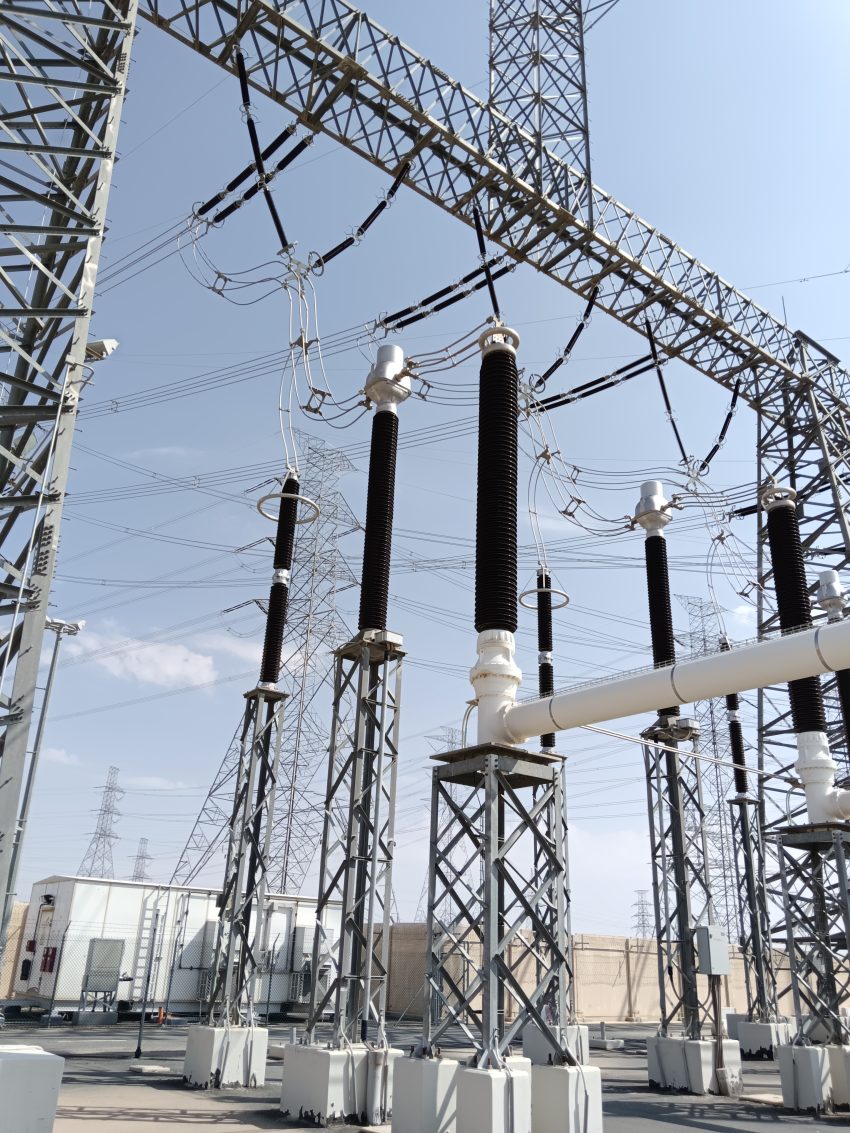
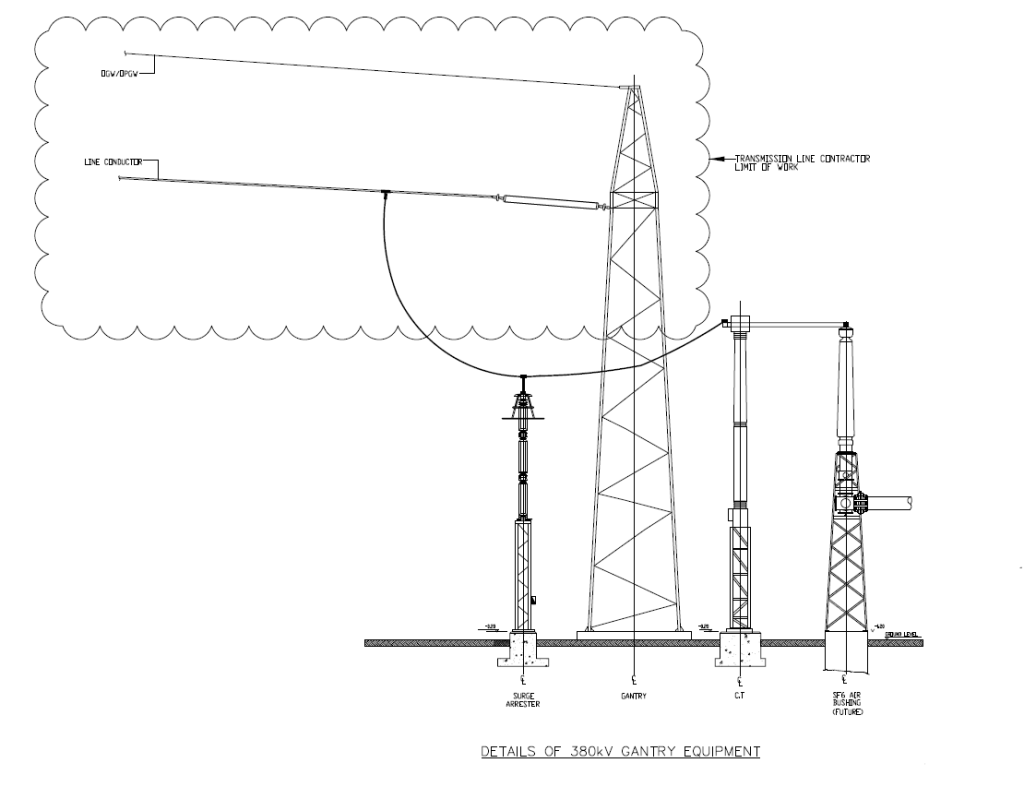
These are tall steel structures that support the incoming 380 kV overhead transmission lines from the grid or other substations. Below Figure shows a 380kV Gantry Structure.
What a Gantry Does
- Supports Conductors:
- Carries incoming or outgoing transmission lines into the substation.
- Maintains proper phase spacing and height clearance. Also provides safe working space for live-line maintenance.
- Transition Point:
- Marks the point where an overhead transmission line terminates inside the substation.
- Lightning Protection:
- Includes overhead shield wires to protect the line entrance.
- Mechanical Strength:
- Withstands the pull of conductors and environmental loads (wind, storms).

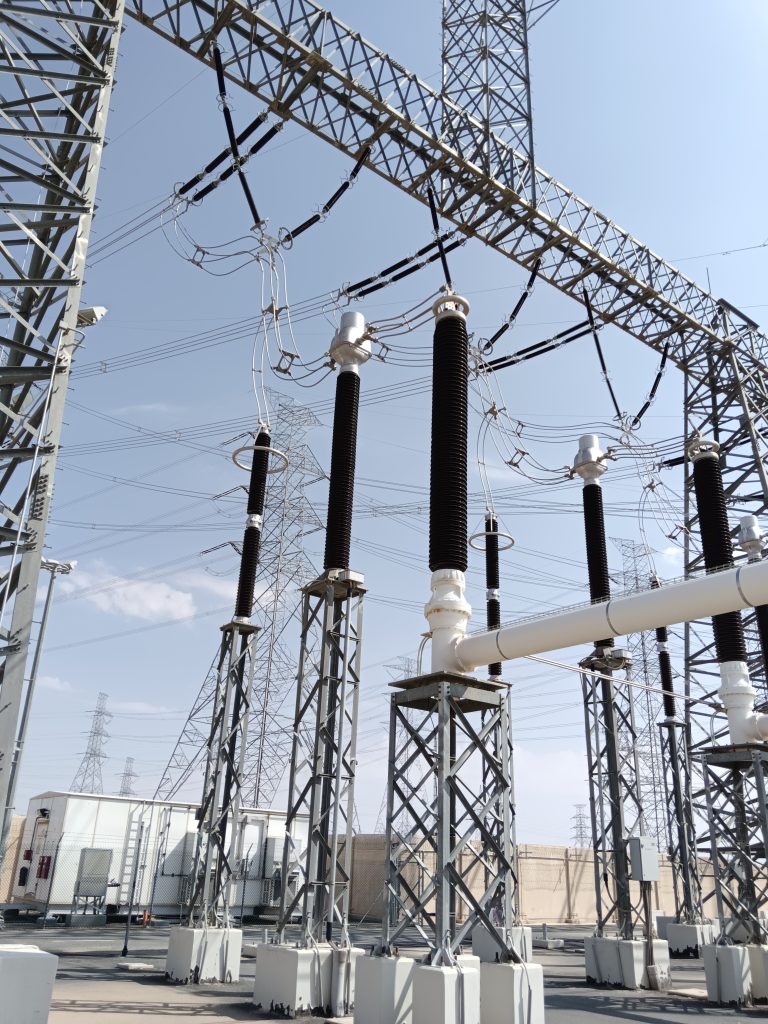
Gantry Equipment
Normally in PTS, Equipment like Surge Arresters, Current Transformers, SF₆ Air Bushing, Voltage Transformers & Cable Sealing Ends, that are installed nearby gantry are termed as gantry equipment. Figure below shows a clear arrangement of a 380kV Gantry Equipment (SA, FCT & SF6/Air Bushing)
- Surge Arresters
- Installed immediately after the line enters the substation.
- Its purpose is to protect equipment from lightning surges and switching overvoltages by diverting surge energy safely to ground.
- Current Transformer (CT)
- Measures current for metering, control, and protection.
- Scales down the high current of the 380kV line to a manageable value for relays and meters.
- Normally as per SEC Practice FCT for metering, control, and protection is Provided insid GIS and outdoor Free standing CTs are required for TEE Protection.
- Voltage Transformer (VT)
- Measures current for metering, control, and protection.
- Scales down the high current of the 380kV line to a manageable value for relays and meters.
- Normally as per SEC Practice VT is Provided insid GIS and outdoor Free standing CTs are not commonly used
- SF₆ Air Bushing
- A bushing is an insulating device that allows a high-voltage conductor to pass safely through grounded enclosures (like a transformer tank, circuit breaker housing, or GIS wall).
- In the case of SF₆ GIB or GIS equipment, the inside is filled with SF₆ gas (for insulation and arc-quenching). But when this equipment connects to overhead lines or outdoor busbars, you need a transition between:
- SF₆ insulation (inside the breaker/GIS)
- Air insulation (outside in the switchyard)
- That’s exactly what an SF₆-to-Air Bushing does:
- One end is mounted inside the SF₆-filled chamber. The other end protrudes into the open air, where it connects to conductors or busbars. It provides safe dielectric insulation across the interface.

Interface Between OHTL Contractor and BSP Contractor
As we describe earlier in our post Gantry Serve as termination points for overhead transmission lines (OHTLs) entering the substation at 380kV. Below Diagram clearly shows the limit of work between an OHTL Contractor & a Substation/BSP Contractor.
Below are Related Posts you may like
- Main Components of Substation-Power Transformers
- Panels Required in Substations
- Transmission lines design important points
- Most Common Electrical engineering interview questions
Following are top Catogories of our Posts

