Learning data structures in C++ is one of the most important steps for anyone looking to become a skilled programmer or software engineer. Data structures provide systematic ways to store and organize data, making programs faster and more efficient. With C++, you can implement data structures in two powerful ways: by building them from scratch or by using the Standard Template Library (STL), which offers ready-to-use implementations. From arrays, linked lists, and stacks to advanced trees, graphs, and hash maps, this guide will introduce the essential C++ data structures with examples to help you strengthen your problem-solving skills, prepare for coding interviews, and apply them in real-world projects.
What is STL in C++ :
The Standard Template Library (STL) in C++ is a powerful set of template classes that provide common data structures and algorithms. It helps programmers save time by reusing well-tested components instead of writing everything from scratch. STL mainly consists of containers, algorithms, iterators, and functors.
Data Structures in C++
A data structure is a way of organizing and storing data so it can be used efficiently.
In C++, common data structures include arrays, linked lists, stacks, queues, trees, graphs, and hash tables.
With STL, many of these are already implemented, such as:
- Vector (dynamic array)
- List (doubly linked list)
- Stack and Queue
- Set and Map (associative containers)
These tools allow developers to handle data effectively and apply algorithms like searching, sorting, and traversing with ease.
Here’s a short comparison table for the mentioned STL containers in C++:
| Container | Type | Key Features | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vector | Dynamic Array | Stores elements in contiguous memory Fast random access (O(1)) Insertion/deletion at end is fast, but slow in the middle | When frequent random access is needed |
| List | Doubly Linked List | Each element has pointers to prev & next No random access Fast insertion/deletion anywhere (O(1) with iterator) | When frequent insertions/deletions are needed |
| Stack | Container Adapter | LIFO (Last In, First Out) push(), pop(), top() | Undo operations, expression evaluation |
| Queue | Container Adapter | FIFO (First In, First Out) push(), pop(), front(), back() | Task scheduling, order processing |
| Set | Associative Container | Stores unique, sorted elements Based on balanced BST Fast search (O(log n)) | When unique, sorted data is needed |
| Map | Associative Container | Stores key–value pairs, sorted by key No duplicate keys Fast search/retrieval (O(log n)) | Dictionaries, key-value |
C++ Vectors: Basic to Advanced:
1. What is a Vector? (Basics)
- A vector is a dynamic array in C++ provided by the Standard Template Library (STL).
- Unlike regular arrays, vectors can resize automatically when you add or remove elements.
- Elements are stored contiguously in memory → random access is fast (
O(1)time).
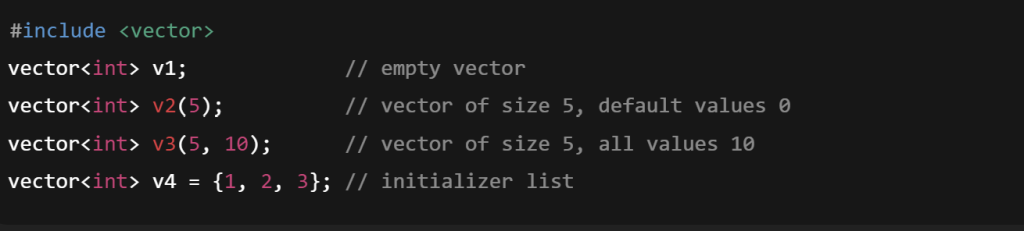
Declaration:
vector<int> v1; // empty vector
vector<int>v2(5); // vector of size 5, default values 0
vector <int>v3(5, 10); // vector of size 5, all values 10
vector<int> v4 = {1, 2, 3}; // initializer list
Insert elements:
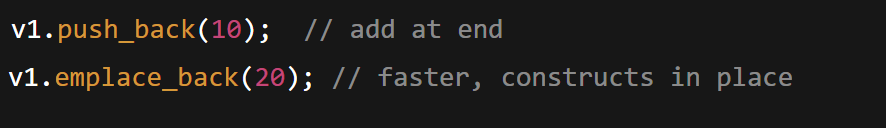
v1.push_back(10); // add at end
v1.emplace_back(20); // faster, constructs in place
Access elements:
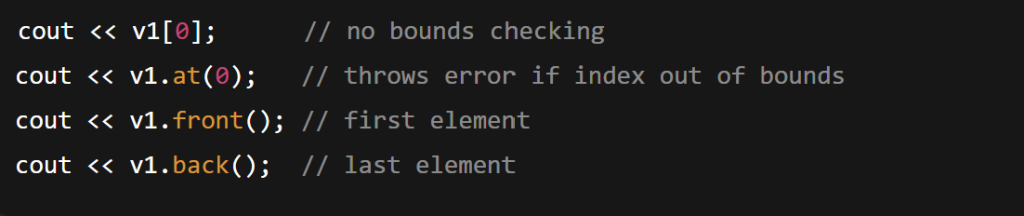
cout << v1[0]; // no bounds checking
cout << v1.at(0); // throws error if index out of bounds
cout << v1.front(); // first element
cout << v1.back(); // last element
Remove elements:
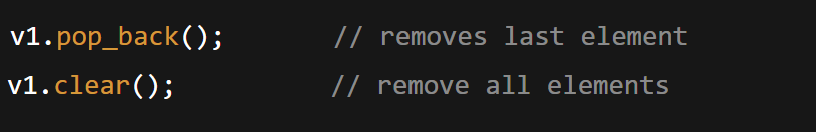
v1.pop_back(); // removes last element
v1.clear(); // remove all elements
Size and capacity:
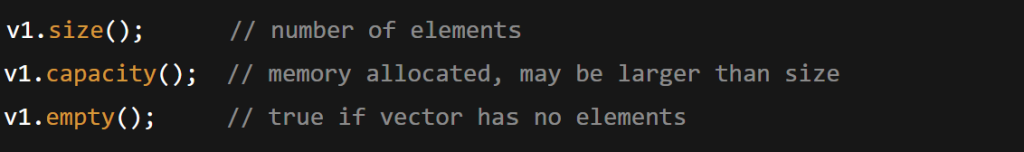
v1.size(); // number of elements
v1.capacity(); // memory allocated, may be larger than size
v1.empty(); // true if vector has no elements
Loops:
for (int i = 0; i < v1.size(); i++)
cout << v1[i] << ” “;
Range-based for loop
for (int x : v1)
cout << x << ” “;
Using iterators:
for (auto it = v1.begin(); it != v1.end(); ++it)
cout << *it << ” “;
Common STL Functions (DSA useful):
Sorting:

Searching:

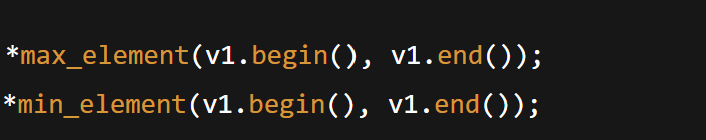
Max/Min:
Advanced Vector Usage (DSA Patterns):
2D Vectors Like 2D Array :
- A vector of vectors → useful for matrices, graphs, DP tables
vector<vector<int>> matrix(3, vector(4, 0)); // 3×4 matrix of 0s
matrix[1][2] = 5; // set element

Dynamic Resizing & Memory
- Vectors automatically resize when
push_backexceeds capacity. v.reserve(n)→ pre-allocate memory to reduce resizing overhead.v.shrink_to_fit()→ reduce capacity to current size.
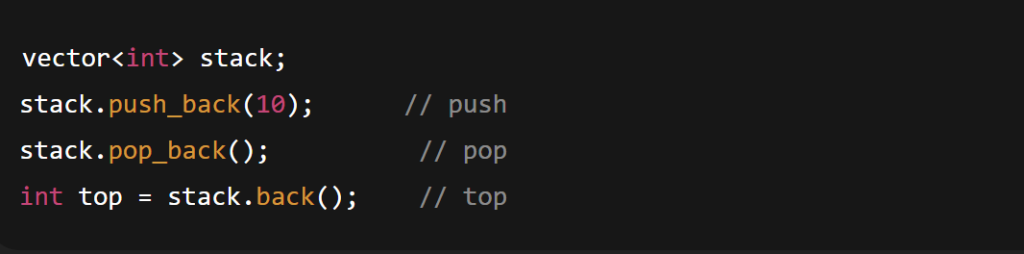
Stack / Queue using vector:
vector<int> stack;
stack.push_back(10); // push
stack.pop_back(); // pop
int top = stack.back(); // top
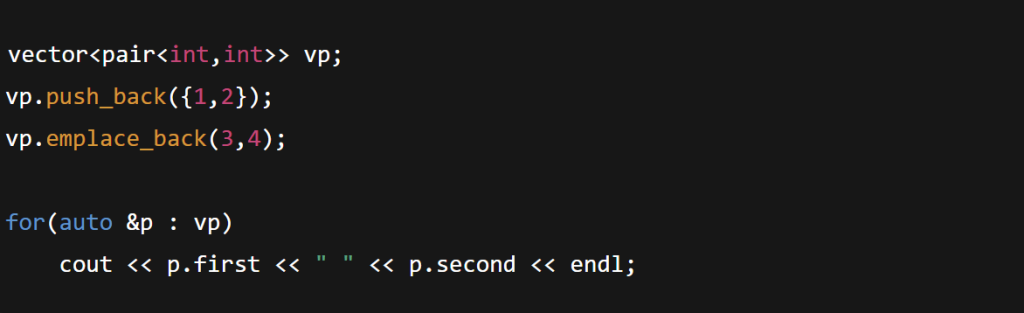
Vector of Pairs:
vector<pair<int,int>> vp;
vp.push_back({1,2});
vp.emplace_back(3,4);
for(auto &p : vp)
cout << p.first << ” ” << p.second << endl;
Vector of Custom Objects:
struct Point { int x, y; };
vector <point> points;
points.push_back({1,2});
points.emplace_back(Point{3,4});

Common Mistakes in DSA:
- Accessing
v[i]whenvis empty usev.at(i)for safety. - Forgetting that
vectorindices start at 0. - Using
push_backin a loop over empty vector incorrectly (common for beginners). - Using
size()in loop asint→ better to usesize_tto avoid warnings:
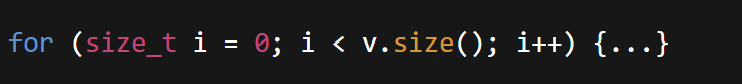
TASKs:
- Write a program to input
nintegers into avector<int>and print them. //easy no solution - Write a program to find the maximum and minimum element in a vector. //easy no solution
- Write a program to reverse a vector without using the built-in
reverse()function. //easy no solution - Write a program to search for an element in a vector (linear search).
- Write a program to remove duplicate elements from a vector.
- Write a program to sort a vector in ascending order using
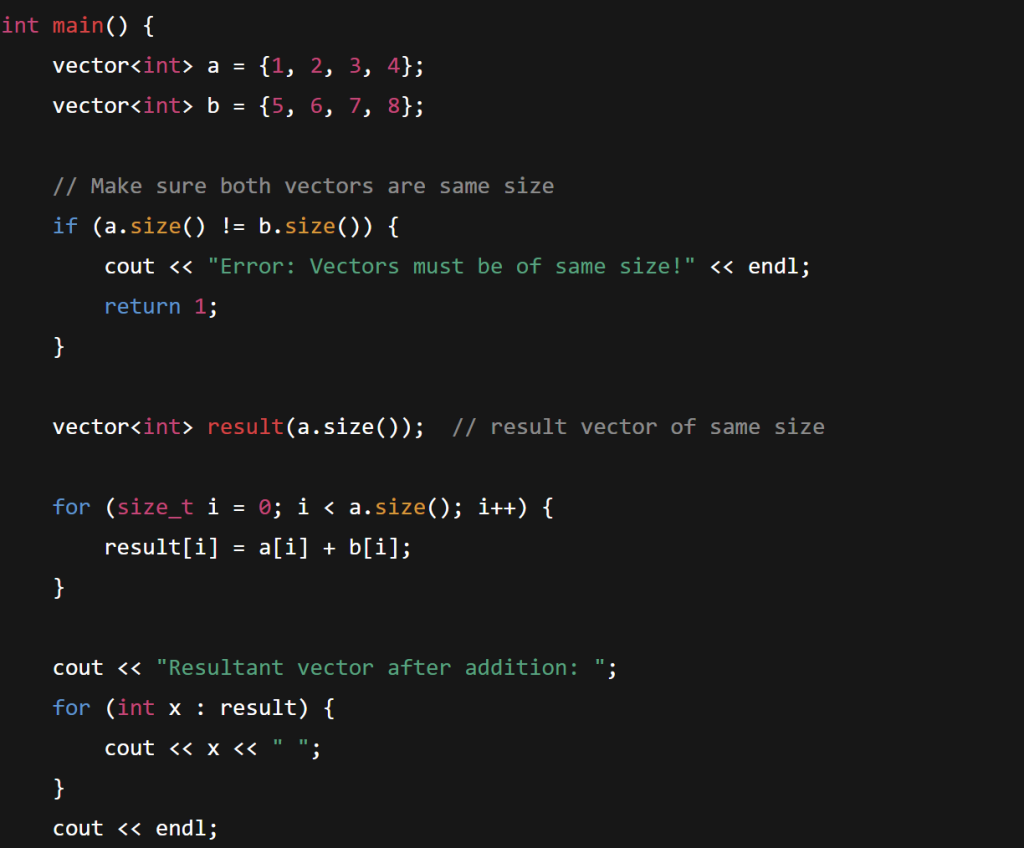
sort(). //easy no solution - Write a program to add two vectors element-wise and store the result in a new vector.
- Write a program to rotate a vector
ktimes to the right.
Solution:
Code is not provided in soft form because you copy code and not write on your own
Write a program to search for an element in a vector (linear search).
solution:

Write a program to remove duplicate elements from a vector.
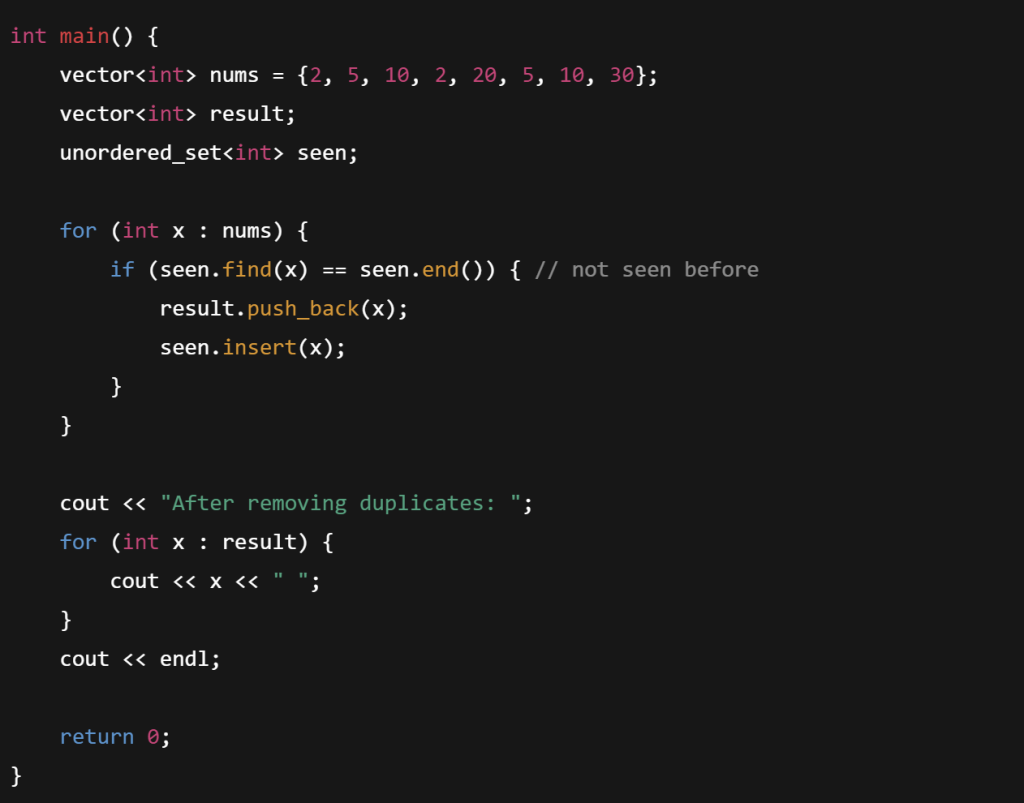
Write a program to add two vectors element-wise and store the result in a new vector.
Write a program to rotate a vector k times to the right.
