In modern power systems, maintaining voltage stability and reactive power balance is becoming more challenging — especially with the increasing share of renewable energy.
Several technologies are used to provide reactive power support and grid stability. The most common ones are:
- Synchronous Condenser
- STATCOM (Static Synchronous Compensator)
- STATCOM with BESS (Battery Energy Storage System)
- SVC (Static Var Compensator)
Each of these solutions has its own advantages, depending on the type of system and performance requirements. In this Post we will provide you an overview of each of these technologies.
Synchronous Condenser
A synchronous condenser is basically a synchronous motor running without a mechanical load, supplying or absorbing reactive power as needed. It behaves like a generator connected to the grid, providing inertia and improving short-circuit strength.
Key Benefits:
- Provides inertia, which helps with frequency stability — a feature power electronic devices lack.
- Improves short-circuit power, helping protection systems to operate correctly.
- Can handle temporary overloads better than static systems.
- However, it has higher losses and a larger footprint compared to static devices.
Best suited for: Weak grids and systems with high renewable penetration, where inertia and fault current support are important. In below link we have provided a detailed post on Challenges in Renewable-Dominated Grids & Role of Synchronous Condensers
Role of Synchronous Condensers in Modern Power Systems (2025)
STATCOM (Static Synchronous Compensator)
A STATCOM is a power electronic device (using IGBTs or similar switches) that provides fast and continuous reactive power support. It can inject or absorb reactive current almost instantly.
Key Benefits:
- Very fast response time for voltage regulation.
- Excellent dynamic reactive power support.
- Compact footprint compared to rotating machines.
- Does not provide inertia or short-circuit current.
Best suited for: Voltage regulation in transmission and distribution networks, especially where space is limited and fast response is needed.
STATCOM with BESS (Battery Energy Storage System)
This is an enhanced version of STATCOM that includes battery storage. It combines the fast reactive support of STATCOM with active power support from batteries.
Key Benefits:
- Provides frequency stability by supplying or absorbing active power.
- Combines dynamic reactive power and energy storage in one system.
- Fastest voltage regulation among all technologies.
- Slightly more complex and costly than standalone STATCOM.
Best suited for: Renewable-rich grids where both voltage and frequency support are required.
SVC (Static Var Compensator)
An SVC is a thyristor-based system (TCR/TSC) used for reactive power compensation. It’s an older technology compared to STATCOM but still widely used.
Key Benefits:
- Reliable and well-proven technology.
- Provides good reactive power support.
- Slower response time than STATCOM.
- No inertia or short-circuit contribution.
- Larger footprint compared to STATCOM.
Best suited for: Bulk power transmission systems where response speed is not critical but cost and reliability are key.
Our Most Read Posts
- Inside a 380kV BSP: Overall Layout Drawing Explained
- 380kV Gantries & Gantry Equipment
- List of Contractors who Won Major BSP Projects in 2024 in KSA
- Tower Testing in Power Transmission: A Complete Guide
- Top Electrical Engineering Courses on Coursera
- List of Top Substation contractors in KSA
- Vector Group of Transformers
- Top Excel Functions Every Engineer Should Master
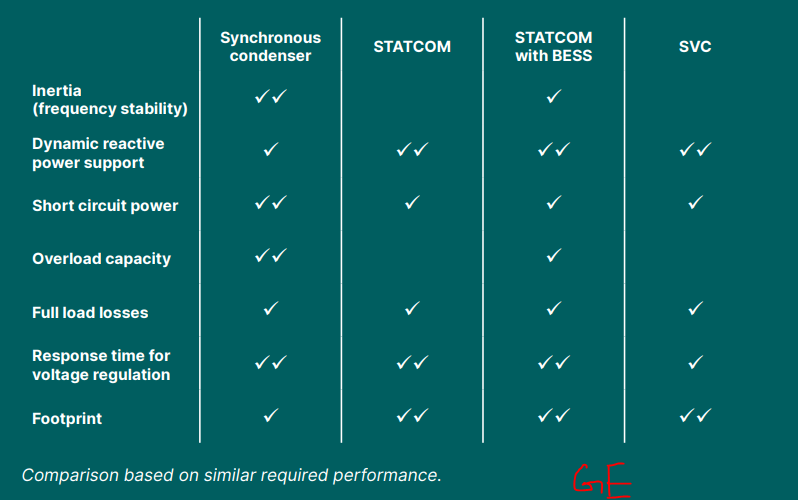
Synchronous Condenser, STATCOM, STATCOM with BESS, and SVC
| Feature | Synchronous Condenser | STATCOM | STATCOM + BESS | SVC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inertia (frequency stability) | ✅✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ |
| Dynamic reactive power support | ✅ | ✅✅ | ✅✅ | ✅✅ |
| Short circuit power | ✅✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
| Overload capacity | ✅✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
| Full load losses | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Response time for voltage regulation | ✅✅ | ✅✅✅ | ✅✅✅ | ✅ |
| Footprint | Large | Small | Small | Medium |
Choosing the Right Solution
| Scenario | Recommended Solution |
|---|---|
| Weak grid, low inertia | Synchronous Condenser |
| Fast voltage regulation | STATCOM |
| Renewable integration (voltage + frequency support) | STATCOM with BESS |
| Cost-effective large grid compensation | SVC |
Conclusion:
Each of these technologies plays a vital role in ensuring grid stability.
- Synchronous condensers are ideal for adding inertia and fault current.
- STATCOMs shine where speed and compactness are needed.
- STATCOM with BESS is the future-ready hybrid for smart grids.
- SVCs remain a proven and economical choice for traditional systems.